1 frank invasion is regarded as the most. The distinction between reactive mesothelial hyperplasia mh and malignant mesothelioma mm may be very difficult based only on histologic and morphologic findings.

Table 4 From The Use Of Immunohistochemistry To Distinguish Reactive Mesothelial Cells From Malignant Mesothelioma In Cytologic Effusions Semantic Scholar
Ema ve 100 vs.

Mesothelioma vs adenocarcinoma ihc. Cell membranes are closely apposed. However only 50 of adenocarcinoma cases stained in this manner. Of 217 cases circulated among all members of the uscanadian mesothelioma reference panel there was some disagreement about whether the process was benign or malignant in 22 of cases.
Diagnosing mesothelioma vs adenocarcinoma. Desmin ve 5 vs. Peritoneal mesothelioma showed reactivity for ck 28 of 28 cases ema 24 of 28 cases am five of 28 cases ca 125 four of 28 cases and s 100 protein three of 28 cases but lacked b723 plap.
Serous carcinoma was reactive for neutral mucins whereas mesothelioma was not. 10 p53 ve 50 vs. The best discriminators among the antibodies considered to be negative markers for mesothelioma are cea moc 31 ber ep4 bg 8 and b723.
A mesothelioma diagnosis can be confused with lung cancer as they have similar sets of symptoms. After analyzing the results it is concluded that calretinin cytokeratin 56 and wt1 are the best positive markers for differentiating epithelioid malignant mesothelioma from pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Mesothelioma vs adenocarcinoma immunohistochemistry.
Most often doctors identify mesothelioma because of other problems the diseases cause. S traight microvilli of variable length less prolific than in mesotheliomas and confined to the apical surface. They may be confined to the apical surface may also be present on the basal surface or may cover the entire.
A history of asbestos exposure is a huge indicator for doctors to look for mesothelioma traits. The above are not very useful in individual cases. A simple pankeratin is useful for seening where epithelial cells are.
Ihc mesothelioma versus mesothelial hyperplasia. Typically ve in adenocarcinoma. Glut1 ve 50 vs.
Intracytoplasmic lumina are absent. L ong slender branching microvilli. Entra para leer el articulo completo.
Claudin4 immunohistochemistry effectively distinguishes adenocarcinoma from malignant mesothelioma with high sensitivity 100 and specificity 99 p 0001 and shows a characteristic membranous staining pattern that was moderate to strong in intensity even in sparsely cellular cell block sections. We evaluated the sensitivity and specificity of 10 monoclonal and two polyclonal antibodies for distinguishing epithelioid mesothelioma from adenocarcinoma adca using immunohistochemistry ihc.

Immunohistochemistry In The Distinction Between Malignant Mesothelioma And Pulmonary Adenocarcinoma A Critical Evaluation Of New Antibodies Journal Of Clinical Pathology
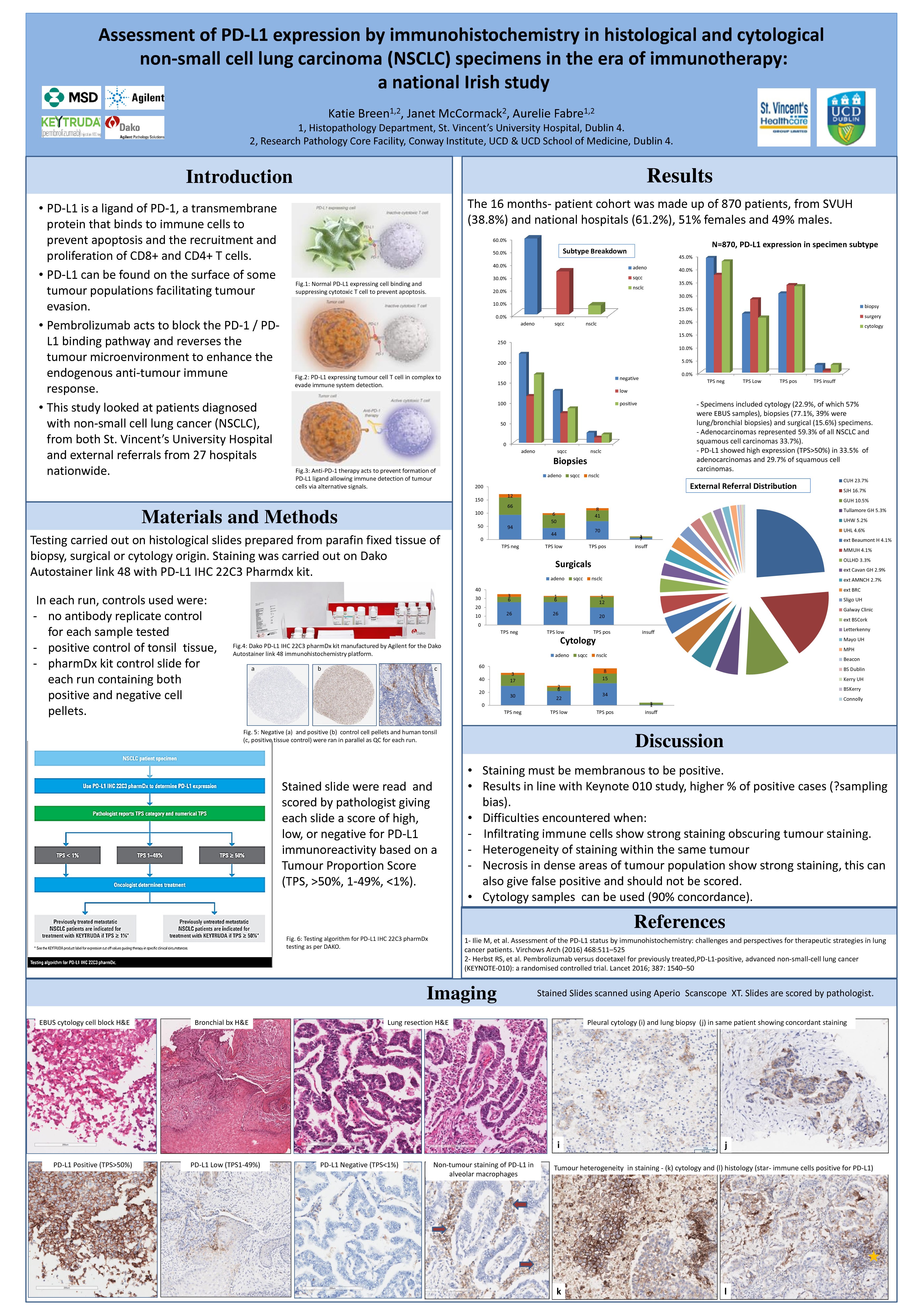
4p Assessment Of Pd L1 Expression By Immunohistochemistry In Histological And Cytological Non Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Nsclc In The Era Of Immunotherapy A National Irish Study Elcc 2018
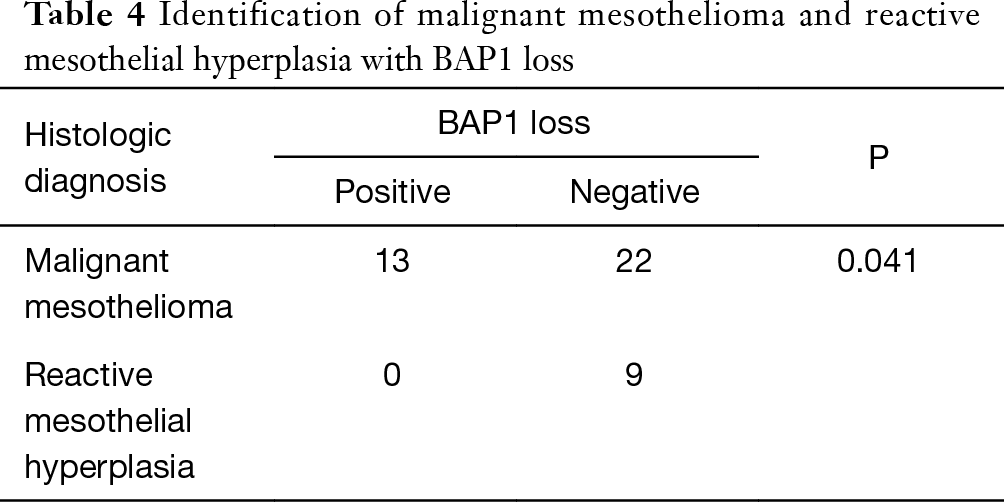
Role Of P16 Deletion And Bap1 Loss In The Diagnosis Of Malignant Mesothelioma Liu Journal Of Thoracic Disease
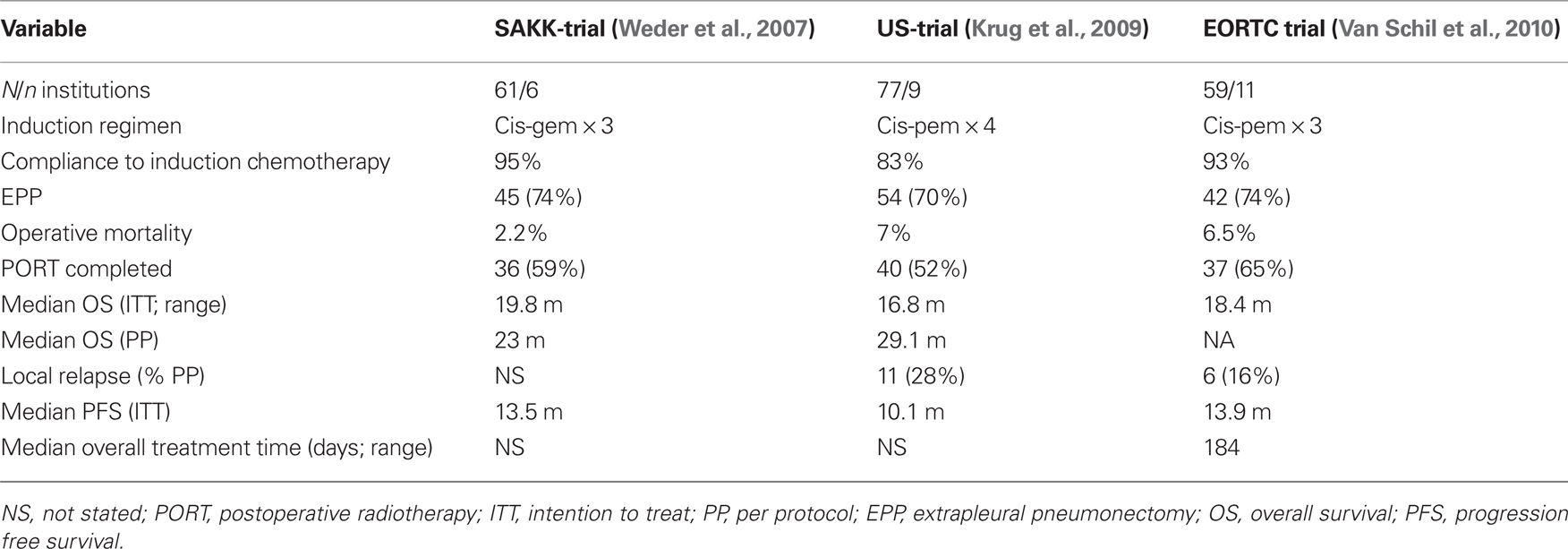
Frontiers Investigational Approaches For Mesothelioma Oncology

How To Add An Idl File To A Visual Studio Project Data Distribution Service Dds Community Rti Connext Users
Http Handouts Uscap Org 2016 Cm06 Dacic 1 Pdf

Table 1 From Sensitivity And Specificity Of Immunohistochemical Markers Used In The Diagnosis Of Epithelioid Mesothelioma A Detailed Systematic Analysis Using Published Data Semantic Scholar
