Negative for malignant cells. Survival from time of initial thoracentesis was directly correlated with pleural ph and decreased pleural fluidserum glucose ratios but was not.

Reliability Of P 16 Calretinin And Claudin 4 Immunocytochemistry In Diagnostic Verification Of Effusion Cytology
Trauma with air in the pleural cavity.

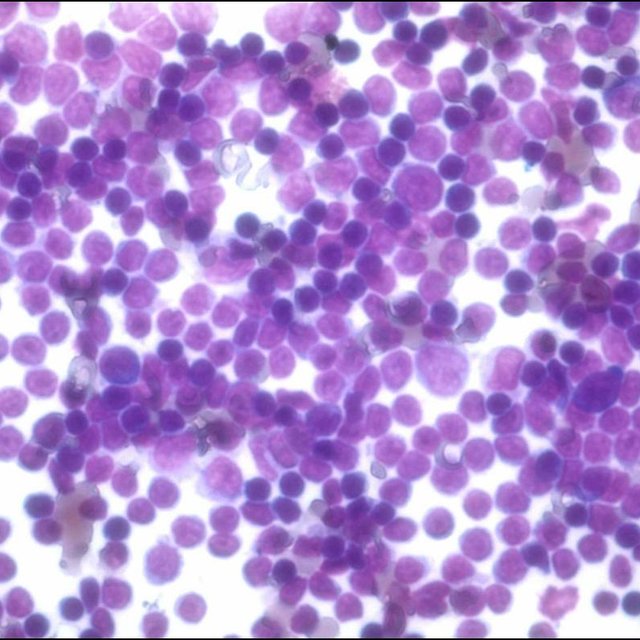
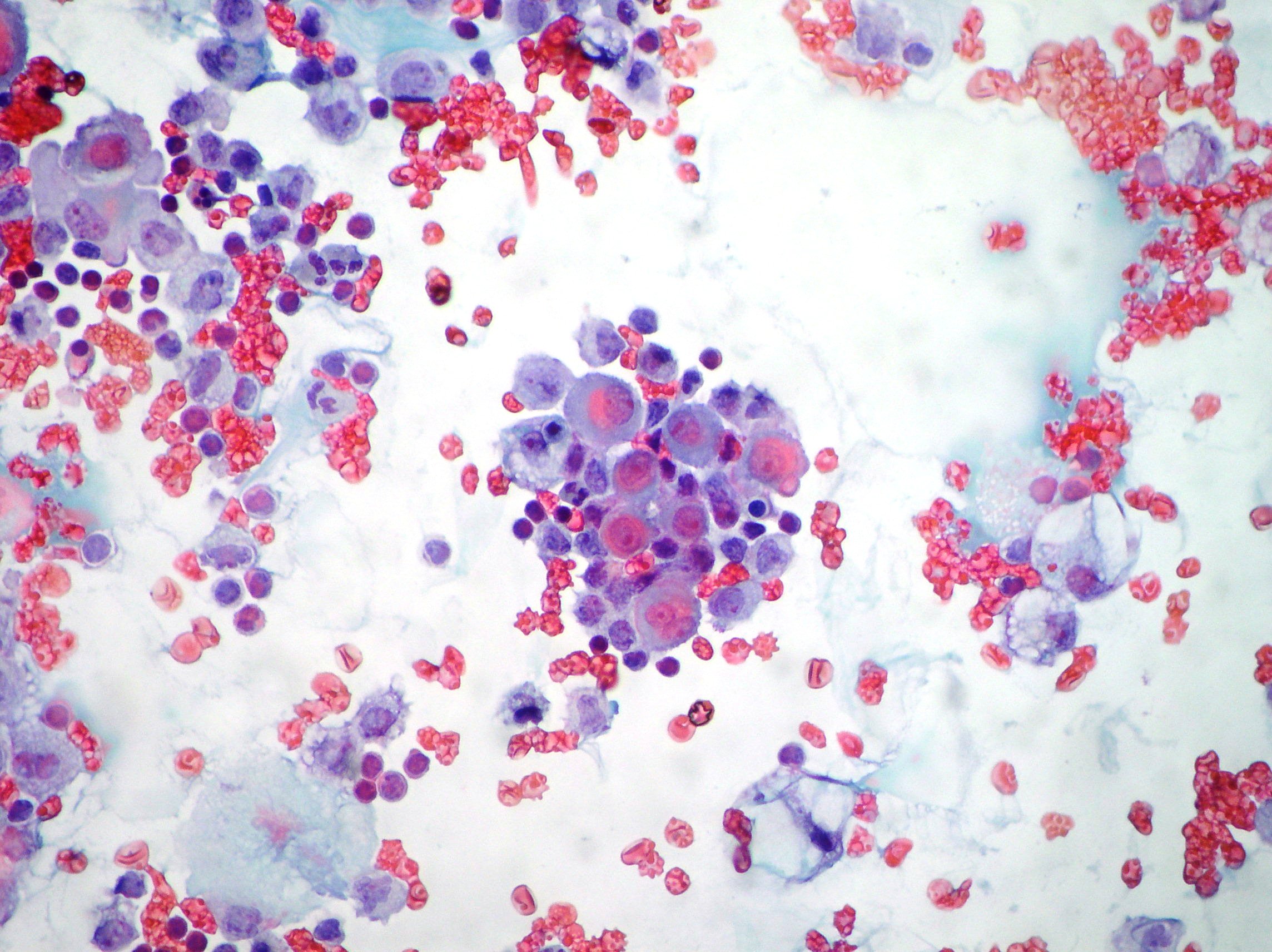
Malignant mesothelial cells in pleural fluid. Even an extremely high pleural fluid ana 1640 can occur in malignant effusions. 625 and 1 416. Neoplastic transformation of mesothelial cells results in malignant mesothelioma an aggressive tumor especially the pleura.
This has a large ddx. Specific diagnoses benign eosinophilic pleuritis general. Reactive mesothelial cells reactive mesothelial cells in pleural fluid reactive mesothelial cells are found when there is infection or inflammation present in a body cavity.
This is known as pleural effusion. Pleural fluid right thoracentesis. A pleural effusion is a buildup of extra fluid in the space between the lungs and the chest wall.
About half of people with cancer develop a pleural effusionwhen cancer grows in the pleural space it causes a malignant pleural effusion. Pleural fluid from patients with tuberculosis had cells with patterns 1 914. Malignant pleural effusions are most commonly lymphocytic but they may be neutrophilic or eosinophilic and although the differential cell count may help narrow the differential diagnosis it will not make.
643 and 3 514. This area is called the pleural space. Markedly increased numbers of.
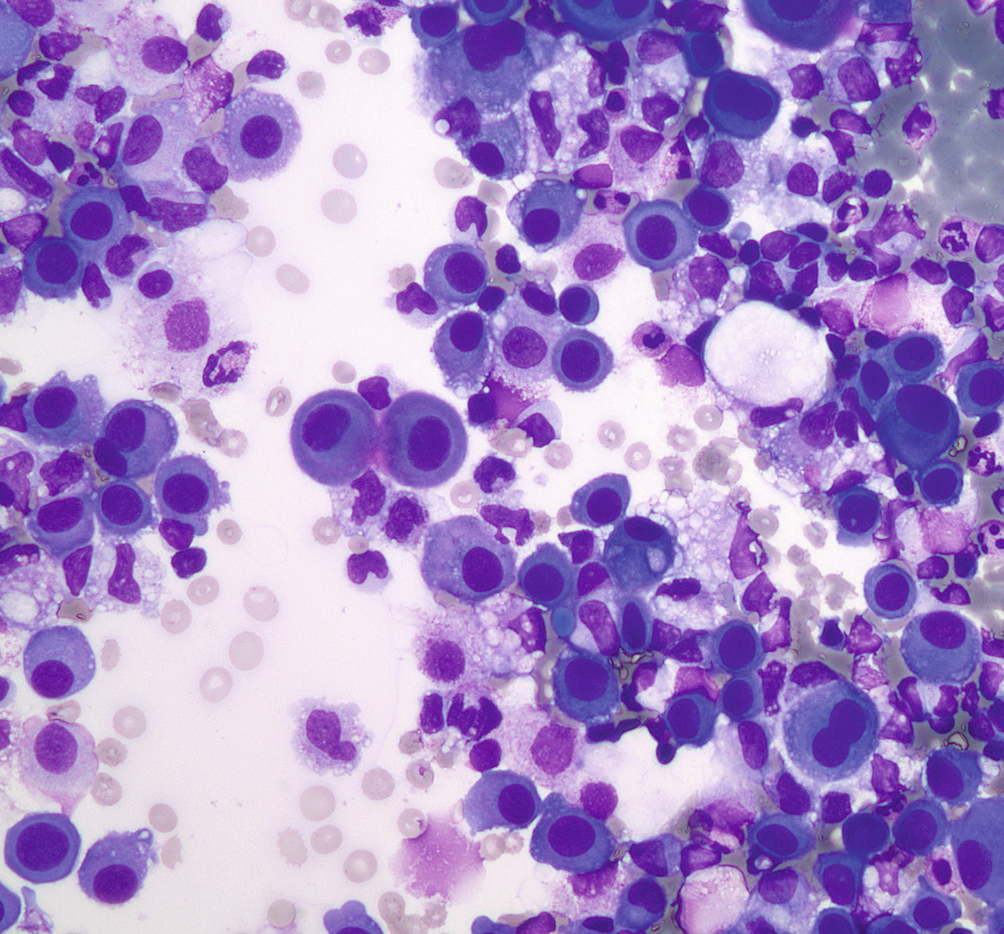
357 whereas most fluid secondary to cancer had cells with patterns 4 1016. Differential cell count a differential cell count on the pleural fluid may help guide the clinician to a specific diagnostic pathway. Population 1 plus cells of variable size and complexity probably corresponding to macrophages and mesothelial cells in fluid.
Pleural fluid characteristics of 26 patients diagnosed with malignant mesothelioma over an 18 year period were reviewed and compared with those of patients with effusions due to other malignancies. This condition is a sign that the cancer has spread or metastasized to other areas of the body. Reactive mesothelial cells present in a background of abundant lymphocytes.
Mesothelial cells are found in variable numbers in most effusions but their presence at greater than 5 of total nucleated cells makes a diagnosis of tb less likely. The fluid can accumulate quickly if the mesothelial cells fail to function resulting in an unhealthy collection of fluids in the chest cavity. A pleural fluid ana titer 1160 however remains a sensitive 86 to 100 percent tool for detecting lupus pleuritis in patients with a known diagnosis of lupus thereby differentiating between lupus pleuritis and other causes of pleural effusions in lupus.
Actively dividing mesothelial cells can mimic an adenocarcinoma. To drain the fluid14 15 in a patient with malignant pleural effusion a pleural fluid ph value less than 730 is associated. A patient may develop shortness of breath and vague chest pains while the fluid experiences a buildup in the chest cavity these are two of the most common.
Additional sampling should be considered within the clinical context.
Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcsfu Mxmneu Gwnfgj0lkypoqodnbul8473zuq95ckzmrca Tnd Usqp Cau
Https Www Rcpath Org Asset Ed8cdd8d 8d04 4b82 Ad48d585e2f023be

Cytology Of Pleural And Peritoneal Lesions Chapter 5 Practical Pathology Of Serous Membranes

Diagnostic Utility Of The Cell Block Method Versus The Conventional Smear Study In Pleural Fluid Cytology Shivakumarswamy U Arakeri Su Karigowdar Mh Yelikar B R J Cytol

Example Of A P16 Deletion Positive Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Download Scientific Diagram